The Ultimate Guide to Garden Planning: How to Use Every Inch and Get Maximum Results
Garden planning is the key to creating a productive, beautiful, and sustainable outdoor space. Whether you’re working with a small balcony garden or a sprawling backyard, strategic planning ensures efficient space utilization, maximum yields, and minimal waste. According to studies, well-planned Office plants can assist in boosting staff well-being by up to 47% according to workplace research carried out at this year’s Chelsea Flower Show. In this guide, we’ll walk you through every step of garden planning, from site selection to garden design, plant choices, and maintenance tips.
Importance of Garden Planning
Before putting a single seed in the ground, taking the time to plan your garden is crucial. A well-thought-out plan ensures efficient use of space, optimal plant growth, and reduced maintenance. With careful garden planning, you can achieve higher productivity, create a visually pleasing layout, and simplify the upkeep.
Garden planning is crucial because:
- Space Optimization: Helps you use every inch of your garden space efficiently, especially if you’re working with a small area.
- Maximized Productivity: When plants are grouped based on their needs (sunlight, water, nutrients), they grow healthier, resulting in higher yields.
- Reduced Maintenance: A well-planned garden minimizes the time and effort required for watering, weeding, and pruning.
- Prevention of Overcrowding: Planning helps avoid overcrowded plantings, which lead to poor air circulation and increased pest problems.
Site Selection and Space Optimization
Choosing the right location for your garden is the first step in ensuring a successful, thriving space. The garden’s location will affect everything from sunlight exposure to water access, soil quality, and air circulation.
Site Selection
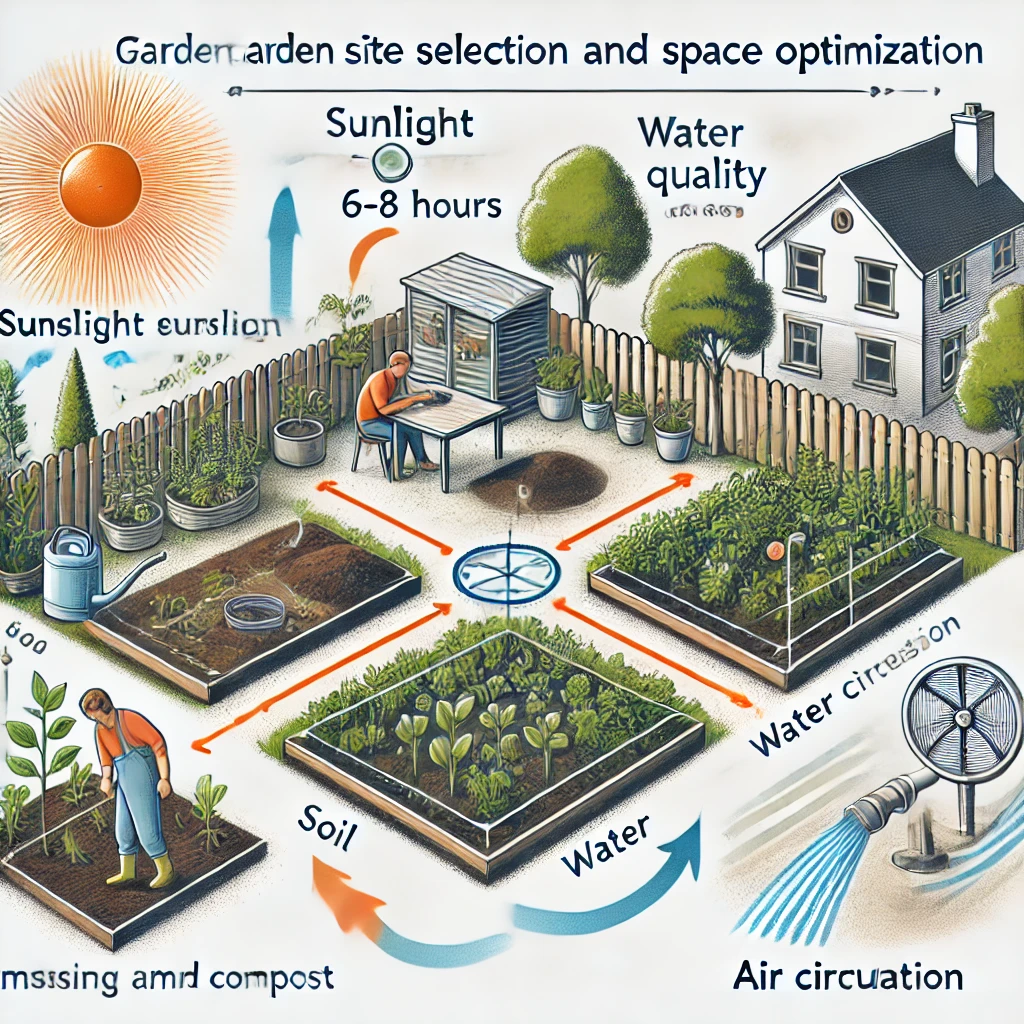
Site selection is crucial for a healthy garden. The placement of your garden should consider several factors such as sunlight exposure, soil quality, and proximity to water. Select a site that receives adequate sunlight, has well-draining soil, and is conveniently located near a water source.
- Sunlight: Most vegetables and flowers require at least 6-8 hours of sunlight daily.
- Soil Quality: Testing your soil is essential. You may need to amend it with compost or organic matter.
- Water Access: Place your garden near a water source for convenient irrigation.
- Air Circulation: Good airflow is essential to prevent diseases and ensure healthy plant growth.
Space Optimization Techniques
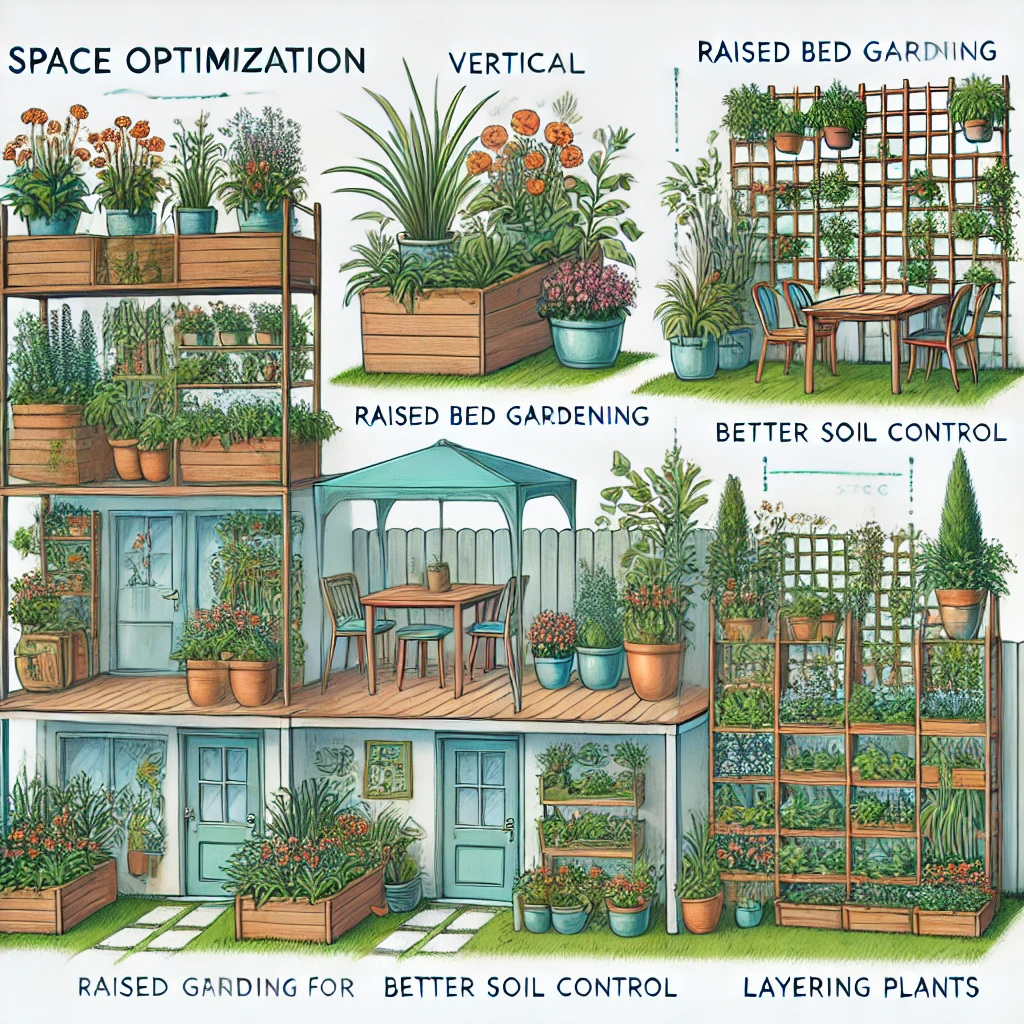

Space optimization is about making the most out of the available area, whether it’s large or small. By using smart planting techniques like vertical gardening or raised beds, you can maximize your growing area.
- Vertical Gardening: Growing plants on trellises and other vertical structures is ideal for small spaces.
- Raised Bed Gardening: Raised beds offer better control over soil quality and drainage, especially in areas with poor soil.
- Container Gardening: Perfect for patios and balconies, containers allow flexibility in plant placement.
- Layering Plants: Utilize different plant heights, with taller plants at the back and shorter ones at the front, to maximize space.
Garden Layout Ideas
Creating the right layout for your garden ensures easy access, healthy plant growth, and efficient use of space. Whether you have a small garden or a large one, planning the layout is essential for its success.
Small Garden Layout Ideas
Designing a small garden requires creativity and strategic space use. Focus on space-saving methods and plants that thrive in small environments.
- Vertical Gardening: Grow climbing plants like beans or flowers on trellises to save ground space.
- Compact Planting: Plant closely together using intensive planting techniques to make the most of every square foot.
- Container Gardening: Group containers together to create a versatile garden on patios, decks, or balconies.
Large Garden Layout Ideas
A large garden offers endless possibilities, allowing for dedicated areas for different plants and activities. Proper zoning and pathways are essential for maintaining such a garden.
- Zoning: Divide your garden into sections like vegetable beds, flower patches, and a relaxation area.
- Garden Paths: Well-planned paths ensure easy access and add structure to the garden. Use durable materials like gravel or stepping stones.
- Focal Points: Add visual interest with water features, rock gardens, or a garden bench as focal points in large spaces.
Choosing the Right Garden Design
Your garden design should match your personal style and the type of space you have. The right design not only enhances the beauty of your garden but also makes it functional and easy to maintain.
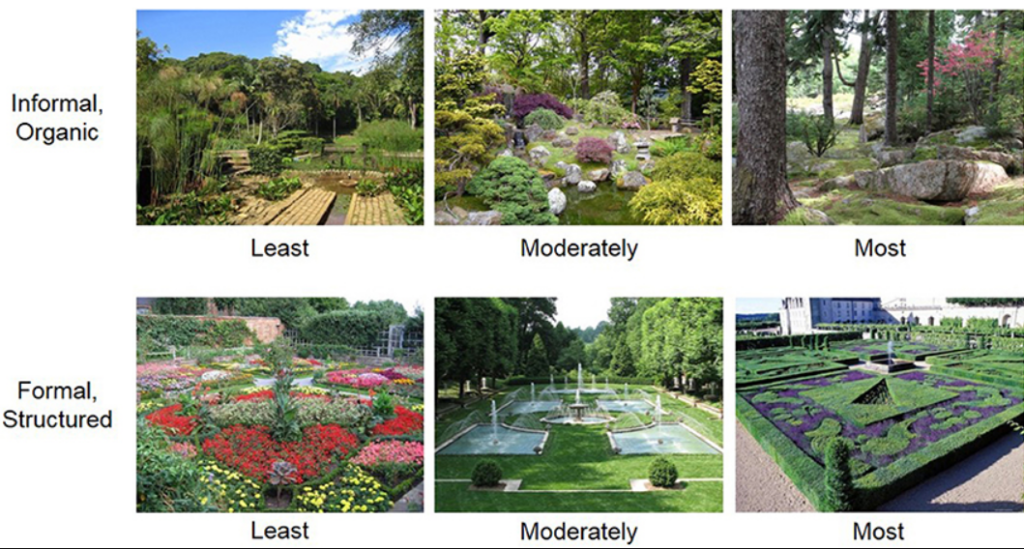

Formal vs. Informal Design
Garden design can be either formal or informal, depending on your preference and space. Each style has its own characteristics that define the layout, symmetry, and plant choices.
- Formal Garden Design: Features symmetrical, straight lines and neatly trimmed hedges. Best suited for large, structured spaces.
- Informal Garden Design: Characterized by free-flowing, natural shapes with curved paths and mixed plantings. Ideal for small or relaxed garden settings.
Popular Garden Themes
Choosing a garden theme allows you to express creativity and tailor the garden to your preferences. From an English cottage garden to a water garden, themes add personality to your space.
- English Cottage Garden: A charming mix of flowers, herbs, and vegetables planted closely together.
- Rock Garden: Uses drought-tolerant plants and stones to create a low-maintenance feature.
- Water Garden: Incorporates ponds or fountains for a peaceful, serene garden atmosphere.
- Backyard Oasis: A space designed for relaxation, with cozy seating areas, garden furniture, and decorative elements.
Maximizing Garden Space
Maximizing your garden space ensures that you can grow more plants and have a more productive garden, no matter its size. Using clever planting techniques and smart layouts helps you make the most of your available area.
Space-Saving Techniques
Using efficient planting techniques can increase your garden’s productivity, especially if you’re working with limited space. Here are some of the best space-saving strategies:
- Square Foot Gardening: Dividing your garden into square-foot sections ensures that each plant has the space it needs to grow.
- Succession Planting: Grow fast-growing crops first, then follow them with slow-growing plants to maximize your harvest.
- Companion Planting: Pair plants that complement each other, like basil and tomatoes, to enhance growth and deter pests.
Layered Garden Bed Design
Layering plants within a garden bed can create depth and interest while optimizing space. Taller plants go at the back, with medium-height plants in the middle and shorter plants at the front.
Garden Bed and Path Design
Garden beds and paths are the structural foundation of your garden. A well-planned layout will make your garden more functional and aesthetically pleasing, ensuring easy access for planting, watering, and harvesting.
Garden Bed Design Ideas
The design of your garden beds can vary depending on your garden’s size, soil quality, and personal preferences.
- Raised Beds: Perfect for small spaces, raised beds provide better drainage and allow you to control the soil quality.
- In-Ground Beds: Best suited for large gardens, in-ground beds provide deep soil space for plants with long roots.
Garden Path Design
Paths in your garden are both functional and decorative. They allow you to navigate the garden easily without compacting the soil around your plants.
- Materials: Gravel, stepping stones, or mulch paths add both practicality and style to your garden.
- Placement: Plan paths to ensure they lead to key areas like vegetable beds, compost bins, and seating areas.
Adding Garden Features and Themes
Incorporating features and themes into your garden adds character and makes your space more enjoyable. These elements can be purely aesthetic or functional, depending on your needs.
Garden Features
Adding features to your garden can enhance both its look and usability.
- Water Garden: A small pond or fountain creates a calming focal point.
- Rock Garden: Provides texture and interest, especially in areas with poor soil.
- Seating Areas: Comfortable seating adds a relaxation zone to your garden.
Garden Themes
A theme can tie your garden together and give it a unique personality.
- Herb Garden: Grow fresh herbs like basil, mint, and rosemary for culinary use.
- Flower Garden: Add color and vibrancy with a variety of flowers such as roses, tulips, or marigolds.
- Vegetable Garden: Plan a productive vegetable garden to grow organic produce like tomatoes, lettuce, and carrots.
Gardening Tips for Beginners
If you’re new to gardening, start small and focus on building your skills. With patience and practice, you’ll see your garden flourish.
- Start with Easy Plants: Choose low-maintenance plants like lettuce, marigolds, or radishes to begin with.
- Track Your Progress: Keeping a garden journal helps you monitor planting dates, weather, and growth.
- Learn from Mistakes: Gardening is a process of trial and error. Don’t be afraid to experiment and learn what works best in your space.
Garden Maintenance and Care
Regular maintenance is necessary to keep your garden healthy and productive. Watering, weeding, and pruning are essential tasks for plant health and growth.
Watering
Consistent and adequate watering is crucial for plant growth, particularly during dry spells. Use drip irrigation or soaker hoses to save water and target the roots directly.
Weeding and Pruning
- Weeding: Removing weeds regularly ensures they don’t compete with your plants for nutrients, water, and sunlight.
- Pruning: Regularly trim your plants to remove dead or diseased parts, which will promote healthier growth.
Sustainable Gardening Practices
Sustainability is important in creating an environmentally friendly and resource-efficient garden. By using eco-friendly practices, you can reduce your impact and promote a healthier ecosystem.
Composting
Create your own nutrient-rich compost from kitchen scraps and garden waste. Composting enriches your soil while reducing waste.
Rainwater Harvesting
Set up rain barrels to collect rainwater, which can be used to water your plants and reduce your dependency on municipal water sources.
Native Plants
Use native plants that are adapted to your local climate. They require less water, fertilizer, and maintenance than non-native species.
Conclusion
Planning your garden is a crucial step in ensuring its success. A well-planned garden maximizes space, enhances productivity, and reduces the need for constant maintenance. By focusing on site selection, garden design, space optimization, and sustainable practices, you can create a beautiful, productive garden that thrives year after year.
Next Steps
- Start by sketching out your garden layout.
- Research plants that suit your local climate and growing conditions.
- Consider raised beds, vertical gardening, or containers to make the most of your space.


